
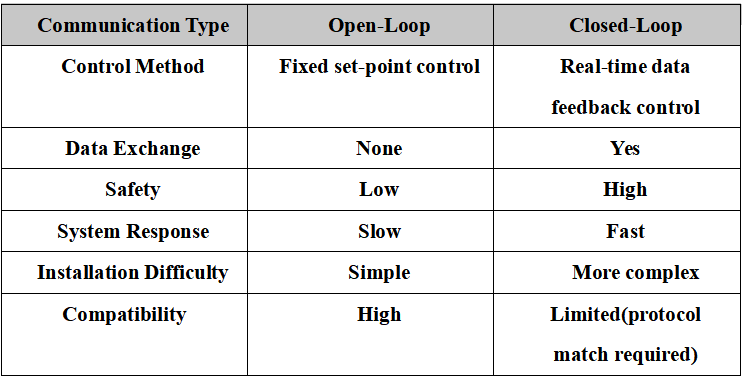
III. Comparison and Summary
Ⅳ. Recommended Application Scenarios
Title
Related Products






